|
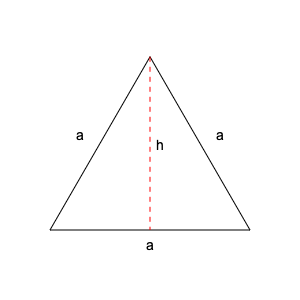
An equilateral triangle is a perfectly symmetrical three-sided polygon with all sides and angles equal, each precisely 60 degrees. This fundamental geometric shape is pivotal in Euclidean geometry, architecture (e.g., truss bridges), and tessellation art. Its structural stability and harmonic symmetry make it ideal for engineering designs, sacred geometry, and natural formations like snowflakes and crystal lattices. The area of an equilateral triangle is calculated using the formula: Area = (√3/4) × side². |
